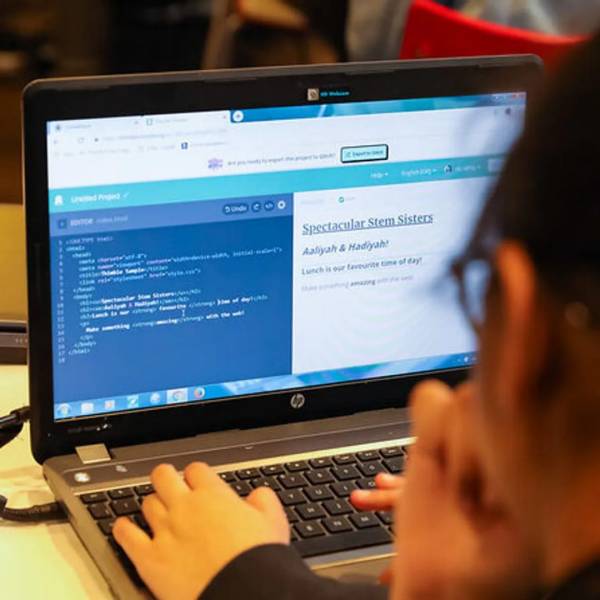
- Backups. Having a backup of your data means having another copy of the data safely stored in case of loss or damage. There are different types of backups that include local backups (backing up data on a floppy disk, CD or hard drive) or cloud backups where your information is kept safely in a remote server that you are able to access. Because cloud backups are digital and can still be accessed if your hardware is lost or damaged, this is the type of backup most used today.

- Encryption. Encryption is the conversion of information from one readable form into another, unreadable form. Most data can be encrypted such as text messages, bank details and pictures. Whilst it doesn’t stop anyone from intercepting your data, it does stop them from reading it.
- Permanent deletion. When you delete an item, it does not actually delete. Instead, it moves it to the trash bin where it becomes accessible to the operating system only because of magnetic traces left on your hard drive. Permanent deletion involves the use of third party software whose sole purpose is to overwrite the data and permanently delete it.
Thank you Holly Walker for taking the Academy stream of Explore through this session.