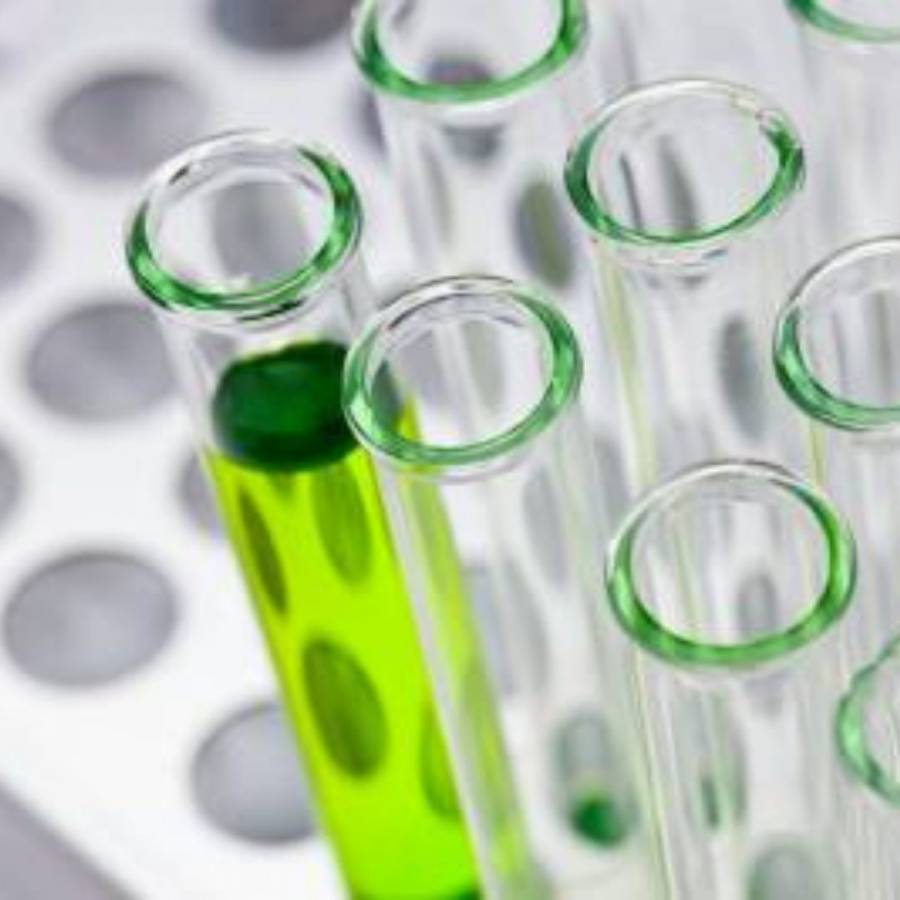
What is Organic Chemistry?
To talk about organic chemistry, we must first talk about organic compounds. So, organic compounds are things that contain carbon that are in covalent bonds. Therefore, organic chemistry looks at these compounds and their physical/chemical properties.
How Does ‘Organic Chemistry’ Get Its Name?
The word organic comes from the fact that all living things or organisms contain water and carbon compounds. An example is fossilised remains in the form of hydrocarbons-natural gas, crude oil, oil shales and coal. They’re also found in carbonates-chalk, limestone and siderite. This involves other sciences like biochemistry, medicine and materials science.
Interesting Facts:
There are many interesting facts about Organic Chemistry:
-
Carbon is visible in its pure form: graphite and diamond.
-
18% of the human body is carbon atoms.
-
Carbon atoms make up the backbone of many important molecules in your body, such as proteins, DNA, mRNA, sugars and fats.
-
These are complex biological molecules, often called macromolecules.
-
Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the universe (fifteenth on Earth and second in the human body, after oxygen).

Who Invented Organic Chemistry?
Organic Chemistry was first founded as a modern science in the 1800s by Jöns Jacob Berzelius. He classified chemical compounds into two groups: organic and inorganic. This separates minerals or non-living matter.
Find out more:
More in Organic Chemistry and careers >>
Read more on the history of Organic Chemistry >>
This piece was written by work experience, Ma’ame.